Why pH Matters Everywhere
pH meters are used everywhere because they provide accurate, crucial measurements of a solution's acidity or alkalinity, which is vital for quality control, product safety, and process efficiency across diverse fields like food production, water treatment, agriculture, medicine, and various manufacturing industries. This precision helps ensure products meet standards, prevents corrosion or contamination, optimizes crop growth, and aids in diagnosing health issues by revealing subtle changes in vital fluids.
Here's why pH meters are so prevalent:
- Quality Control: Many products, from foods and beverages like wine and cheese to cosmetics and detergents, require a specific pH to ensure proper taste, texture, and stability.
- Safety & Health: In medicine, doctors use pH meters to monitor blood and urine pH, as even minor shifts can indicate health problems. In water treatment, pH meters ensure that drinking water is balanced and safe, preventing pipe corrosion from overly acidic water.
- Agriculture: Farmers use pH meters to assess soil acidity, which directly impacts a plant's ability to absorb nutrients and affects crop yields.
- Industry: Industries from pharmaceuticals and biotechnology to paper and steel manufacturing rely on pH meters to control chemical processes, neutralize wastewater, and produce high-quality goods.
- Environmental Monitoring: Beyond municipal water, pH meters are used to monitor groundwater and ensure environmental safety.
- Precision Over Indicators: Unlike pH strips or dyes that provide only a color change, a pH meter gives a precise numerical value, offering a higher level of accuracy and detail for critical applications.
- Versatility: Specialized pH probes are available for measuring a wide range of substances, from liquids and semi-solids like meat and cheese to surfaces like skin, leather, and paper.
How pH Meters Work
The Core Principle: Sensing Hydrogen Ions
Every liquid contains hydrogen ions (H⁺). The more H⁺ ions present, the more acidic the solution (low pH). Fewer H⁺ ions mean alkaline conditions (high pH).
- Acidic solutions (pH 0–6.9) have lots of H+ ions → higher voltage.
- Alkaline solutions (pH 7.1–14) have fewer H+ ions → lower voltage.
A pH meter detects these ions and converts their activity into a voltage, then into a pH number.
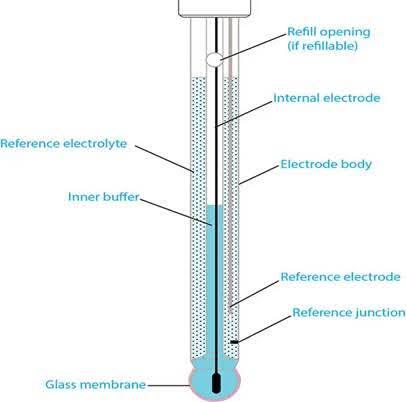
Anatomy of a pH Probe: The 3 Critical Parts
-
Glass Electrode
- A special pH-sensitive glass membrane (often lithium silicate) forms the tip.
- How it works: H⁺ ions in your sample interact with the glass, creating a tiny voltage difference.
- Fun fact: This glass is so thin (0.1 mm) that hydrogen ions can "cross" it!
-
Reference Electrode
- Filled with a stable electrolyte solution (usually 3M KCl).
- Provides a consistent baseline voltage for comparison.
- Key role: Without it, the meter couldn’t "anchor" its measurements.
-
Internal Solutions
- pH 7 buffer: Inside the glass electrode.
- Ag/AgCl wire: Converts ion activity into electrical signals.
How Measurements Happen
-
Dip the Probe
- The glass membrane contacts your sample (e.g., water, soil slurry).
- H⁺ ions interact with the glass surface.
-
Ion Exchange
- H⁺ ions diffuse through the glass membrane, swapping places with lithium ions inside.
- This creates a voltage difference across the membrane.
-
Voltage Generation
- Acidic solutions (high H⁺) → Higher voltage.
- Alkaline solutions (low H⁺) → Lower voltage.
- Critical formula: Δ Voltage = 59.16 mV × ΔpH (at 25°C).
-
Signal Conversion
- The meter’s microprocessor converts voltage into pH using the Nernst equation (automatically!).
- Temperature sensor: Adjusts for temperature’s effect on ion activity.
-
Display
- The pH value appears on-screen (e.g., "pH 5.3").
Why Temperature Compensation is Non-Negotiable
- pH measurements are temperature-dependent.
- Example: Pure water at 25°C has pH 7.0. At 100°C, pH drops to 6.1!
- Solution: All modern meters use ATC (Automatic Temperature Compensation) via a built-in thermometer.
Why Probes Degrade (And How to Save Them)
Glass electrodes aren’t immortal! They fail because:
- Drying out: The gel layer inside dehydrates → slow response.
- Scratches/Cracks: Exposes internal reference solutions.
- Chemical damage: Strong acids/bases corrode the glass.
Fix it:
- Store probes wet in 3M KCl or pH 4.0 buffer.
- Never touch the glass bulb!
- Clean with mild detergent (e.g., for coffee oils) or HCl 0.1M (for mineral scale).
How to Know Your Probe is Healthy
- Response time: Should stabilize in 10–30 seconds.
- Calibration slope: Should be 95–105% during calibration.
- Offset: Should be ±30 mV in pH 7.0 buffer.
How to choose Your Perfect pH Meter
-
Evaluate Your Application & Needs
Type of Meter:
- Pen testers: Ideal for budget-conscious users or simple, at-home testing.
- Portable/Handheld: Offer portability for field use and on-site measurements.
- Benchtop/Laboratory: Best for stationary use in labs, offering high accuracy and features.
- Industrial: Designed for harsh environments like chemical plants or wastewater treatment, requiring robust and durable models.
- Accuracy and Resolution: Higher accuracy (0.01 vs. 0.1) is crucial for applications like pharmaceuticals, while less precise meters may suffice for general purposes.
- Measurement Environment: Consider where you'll be measuring (laboratory, outdoors, industrial) to determine if you need a water-proof (IP-rated), chemically resistant, or otherwise robust meter
To choose the right pH meter, assess your specific application to determine the necessary type (pen, portable, benchtop, or industrial), select the appropriate accuracy and resolution, and consider key features like temperature compensation, electrode type, and data management capabilities. Factor in durability, portability, user-friendliness, and your budget to find a meter that meets your needs for precise, reliable pH measurement.
This video explains how to choose a pH meter for laboratory use:

![]() YouTube• Thermo Fisher Scientific
YouTube• Thermo Fisher Scientific
-
Consider Essential Features
- Temperature Compensation:Automatic Temperature Compensation (ATC) is important for maintaining accuracy across different temperatures, especially in lab or industrial settings.
- Electrode Type & Junction:Choose an electrode with a junction suitable for your sample type. Open or flushable junctions are good for samples with solids, while others are better for general use or low ionic strength.
- Data Management:Look for features like data logging, storage, and connectivity to a computer if you need to track and transfer your pH readings.
- Calibration & Maintenance:Consider how easy the meter is to calibrate and maintain, as this is essential for accuracy.
-
Factor in Practical Aspects
- Durability:Select a meter with good build quality, especially for industrial or field use.
- User-Friendliness:Ease of use is important for efficiency and for high-throughput environments.
- Portability:If you need to measure pH in various locations, a portable or pen-style meter will be more practical.
- Budget:Determine your budget, but remember that a higher-quality meter with better accuracy and durability can save you money in the long run by preventing frequent replacements or errors.
-
Research Support & Warranty
- Customer Support:Look for a manufacturer with a good reputation for reliable customer service.
- Warranty:Ensure the meter is backed by a good warranty to address any future issues.
|
Your Use Case |
Recommended Meter Type |
Budget Range |
Top Features to Look For |
Example Models |
|
Home Water / Pools |
Waterproof Pen Testers |
₹1,500 – ₹7,500 |
Simple calibration, ATC, compact design |
|
|
Gardening/Soil |
Spear-Tip Soil Probes |
₹5,000 – ₹12,900 |
Rugged tip, no slurry needed |
Kelway Soil Meter, Bluelab PENPH |
|
Aquariums/Hydroponics |
Combo Meters (pH + TDS**) |
₹12,900 – ₹19,000 |
Dual readings, waterproof |
Bluelab Combo Meter, Eutech PH Test 30 |
|
Labs/Brewing |
Benchtop or Premium Pens |
₹18,000 – ₹42,000 |
High accuracy, data logging |
Eutech pH 700, Hanna HI5522 |
|
Industrial Use |
Rugged Benchtops |
₹15,000 – ₹85,000+ |
Durable, advanced diagnostics |
Milwaukee MW102 PRO+, Hanna HI5522 |
*ATC = Automatic Temperature Compensation
**TDS = Total Dissolved Solids
Key Features Explained:
- Accuracy: Look for ±0.01 pH for labs, ±0.1 for home use.
- Probe Type: Glass probes (for liquids) vs. spear probes (for soil).
- Waterproof Rating: IP67 or higher for outdoor/pool use.
- Calibration: Auto-calibration saves time; manual is cheaper.
- Connectivity: Bluetooth for data logging to your phone.
Pro Tip: Always budget for calibration solutions and probe storage fluid! A ₹1,700 meter that lacks these might cost more long-term. [Link: Digital pH Meter Price Guide]
2025’s Top 8 pH Meters (Ranked By Use Case)
After testing dozens of models, here are our top picks for 2025:
|
Rank |
Meter & Price |
Accuracy |
Best For |
2025 Game-Changer |
|
1 |
Hanna HI5522 Benchtop pH Meter |
±0.002 |
Research Labs |
Touchscreen + advanced dual-channel functions |
|
2 |
±0.01 |
Labs/Academics |
Affordable lab-grade precision + auto calibration |
|
|
3 |
Bluelab Combo Meter |
±0.02 |
Hydroponics/Aquaponics |
Measures pH, EC & Temp in one compact device |
|
4 |
Milwaukee MW102 PRO+ |
±0.01 |
Industrial |
Rugged design with shock/water resistance |
|
5 |
±0.1 |
Pools/Aquariums |
Simple, waterproof, great entry-level choice |
|
|
6 |
±0.1 |
Field/General Use |
Compact, affordable, easy calibration |
|
|
7 |
Kelway Soil pH Meter |
±0.2 |
Soil/Gardening |
Direct soil testing, no slurry required |
|
8 |
±0.1 |
Home/Water Tanks |
Budget-friendly, routine water checks |
1. HANNA HI98107 pHep® Digital pH Meter – Compact, waterproof, ±0.1 accuracy
2. Eutech pH 700 Benchtop Meter – ±0.01 accuracy, lab use, auto calibration
3. Aquasol Digital pH Meter (Portable) – Affordable, simple calibration, ±0.1 accuracy
4. Hanna HI5522 Research Grade Benchtop Meter – Touchscreen, dual-channel, ±0.002 accuracy
5. Bluelab Combo Meter – pH + EC + Temperature in one device, waterproof
6. Milwaukee MW102 PRO+ – Portable, shock-resistant, ±0.01 accuracy
7. Kelway Soil pH Meter – Direct soil measurement, rugged probe
8. SKY-PH-431 Digital pH Meter – Affordable, for aquariums/pools/home water
You can also refer this blog at our website: https://scispectrum.in/blog/best-digital-ph-meters-for-every-use-case-in-2025-/
Why These Dominate 2025
-
Hanna HI5522
– Research-grade accuracy (±0.002) with dual-channel capability, ideal for regulated laboratories. -
Eutech pH 700
– Reliable ±0.01 precision and multi-point calibration at an affordable price for routine lab use. -
Bluelab Combo Meter
– Simultaneous pH, EC, and temperature readings make it essential for hydroponics and aquaculture.
4. Hanna HI98107 pHep®
– Compact and waterproof, delivering dependable ±0.1 accuracy for pools and aquariums.
|
Use Case |
Top 2025 Pick (Catalogue Product) |
Why It Wins |
|
|
Home / Pools |
Affordable, waterproof, simple one-point auto calibration |
||
|
Gardening / Soil |
Rugged spear tip, ideal for direct soil pH checks (no slurry needed) |
||
|
Aquariums / Hydroponics |
Measures pH + nutrients + temperature, perfect for aquaponics & hydroponics |
||
|
Precision Labs |
Lab-grade accuracy (±0.01), multi-point calibration, reliable for research |
||
|
India Users (Budget-Friendly) |
Affordable, reliable, and designed for routine water checks |
Common pH Meter Mistakes (and How to Avoid Them)

To avoid costly mistakes when buying a pH meter, select a model suited for your specific application, balance cost with necessary features, and consider the long-term costs of calibration and maintenance. Also, prioritize reliability by checking the warranty and customer support. When using the meter, remember to calibrate it properly with fresh buffer solutions, maintain the electrode with proper cleaning and storage, ensure proper electrode submergence, and check for air bubbles.
Before Buying
- Define Your Needs: Determine your primary use case (e.g., laboratory research, field testing, brewing) and select the electrode type best suited for your samples.
- Budget vs. Features: High-end models provide better accuracy and advanced features but at a higher cost. Choose a meter that balances essential features with your budget.
- Calibration & Maintenance: Consider the ease of calibration and ongoing maintenance. Meters with simple calibration procedures and low maintenance save time and reduce long-term costs.
- Reliability & Support: Look for models backed by strong warranties and responsive customer service to ensure long-term reliability.
- Reviews & Recommendations: Check both customer feedback and expert reviews to understand real-world performance and reliability.
- Future-Proofing: Prefer meters that allow upgrades or additional sensors, so your device remains useful as your needs evolve.
Before and During Use
- Calibrate Properly: Use fresh, high-quality buffer solutions and calibrate with at least two points (e.g., pH 4.0 and pH 7.0) to ensure accuracy across your measurement range.
- Maintain the Electrode: Clean the electrode with distilled water between uses and store it in the proper storage solution to keep it hydrated and prevent damage.
- Inspect for Damage: Check the electrode for dryness, dirt, or clogs, as these can lead to slow, erratic, or unreliable readings.
- Handle the Electrode Correctly: Avoid wiping the electrode, as this can introduce contaminants or damage the sensor. Instead, rinse it with distilled water.
- Submerge Adequately: Ensure the electrode is fully submerged in the sample to get an accurate reading.
- Check for Air Bubbles: Air bubbles on the electrode can interfere with the measurement, so check for and remove them
Future Trends of PH Meter
Future pH meter trends for 2025 and beyond include the increased integration of IoT and AI for smart, connected devices, advancements in durable, glass-free sensor technology (such as ISFETs), enhanced automation, automatic calibration features, and a strong emphasis on sustainability. Market growth will be driven by stricter regulations, growing industrialization in regions like Asia-Pacific, and demand for precise and efficient pH measurement in diverse sectors like pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, water treatment, and agriculture.
Technological Advancements
- Smart & Connected Devices:pH meters will increasingly feature integrated sensors, Bluetooth, and cloud connectivity for real-time data sharing, remote monitoring, and integration into larger IoT ecosystems.
- AI Integration:Artificial intelligence will play a larger role in pH meters, enabling advanced features like predictive analytics, real-time diagnostics, and more sophisticated automated calibration processes.
- Advanced Sensors:Solid-state ISFET (Ion-Sensitive Field-Effect Transistor) sensors will become more prevalent, offering better durability, longer lifespan, and glass-free operation, which is ideal for harsh environments and Clean-in-Place (CIP) processes.
- Automatic Calibration:The self-calibrating pH meter market is growing, driven by the need for hands-free, accurate, and efficient operation.
Market Drivers & Applications
- Regulatory Compliance:Stringent food safety, environmental, and industrial standards are increasing the demand for precise and reliable pH measurement.
- Industrial Growth & Digitalization:Automation in manufacturing, water treatment, and other sectors will boost the need for automated and connected pH meters.
- Precision Agriculture:The expansion of precision agriculture is driving demand for on-site, accurate pH measurement.
- Diverse Industries:The pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, water treatment, and agricultural sectors will continue to be major drivers of innovation and adoption.
Sustainability & Design Trends
- Eco-Friendly Models:There will be a greater focus on developing energy-efficient and environmentally friendly pH meter designs.
- Increased Durability:Advancements in sensor technology will lead to more durable and longer-lasting devices, reducing replacement frequency and waste.
Regional Growth
- Asia-Pacific:Rapid industrialization and large-scale water infrastructure projects will make Asia-Pacific a significant growth region for the pH meter marke
FAQs: Quick Answers to Top Searches
Q: Can I use a water pH meter for soil?
A: No! Water probes have fragile glass tips. Use a rugged spear probe for soil. [Link: How to Choose a pH Meter for Soil Testing]
Q: Why does my pH meter show "ERR"?
A: Common causes: dead battery, dried probe, or wrong calibration. Rehydrate the probe or recalibrate.
Q: How often should I replace my probe?
A: Budget pens: 6–12 months. Mid-range: 1–2 years. Lab-grade: 3–5 years.
Q: Is a pH meter better than litmus paper?
A: Yes! Digital meters are faster, more accurate, and work for colored liquids. [Link: What is a Digital pH Meter?]
Q: Do I need a TDS meter too?
A: For hydroponics or aquariums, yes! TDS measures nutrient/impurity levels. [Link: What is a TDS pH Meter?
Q: Do I need to calibrate my pH meter every time?
A: Not always. For critical testing (like labs or hydroponics), calibrate before each session. For casual use, once a week is usually enough.
Q: What’s the best storage solution for a pH probe?
A: Always keep it moist in KCl (potassium chloride) solution. Never store in distilled or RO water — it damages the probe.
Q: Can I test milk, wine, or other thick liquids with a regular pH meter?
A: Standard probes struggle with viscous samples. Use a flat-surface probe or specialized food pH meter for reliable results. [Link: Best Food pH Meters]
Q: Why does my pH meter reading drift up and down?
A: Likely causes: temperature changes, dirty electrode, or unstable sample. Clean the probe, let the sample settle, and use a meter with ATC (Automatic Temperature Compensation).
Q: What’s the difference between a pH pen and a benchtop meter?
A: Pens are portable and affordable but less precise. Benchtop meters are bulkier, pricier, but far more accurate (±0.01 pH).
Q: Can I use one pH meter for all applications?
A: Not really. Soil, food, pools, aquariums, and labs often require different probe types. Choose based on your use case.
Q: How do I clean my pH probe properly?
A: Rinse with distilled water after each use. For tough build-up, use a pH electrode cleaning solution — never scrub with cloth or brush.
Q: What’s ATC in a pH meter?
A: ATC stands for Automatic Temperature Compensation. It adjusts readings for temperature changes so you get accurate results across hot or cold samples.
Q: How long should I leave the probe in the sample?
A: Wait until the reading stabilizes — usually 30–60 seconds. Stir gently to avoid air bubbles.
Q: Are cheap pH meters reliable?
A: They work for casual use but need frequent recalibration and replacement. For serious testing, invest in mid-range or lab-grade models.
Conclusion
pH meters are more than just gadgets they’re essential tools for anyone who needs accuracy, whether in gardening, cooking, brewing, or lab work. By choosing the right meter, calibrating it regularly, and storing it properly, you can trust your readings every time. As technology evolves, pH meters are becoming smarter, tougher, and easier to use, making reliable testing accessible to everyone.
